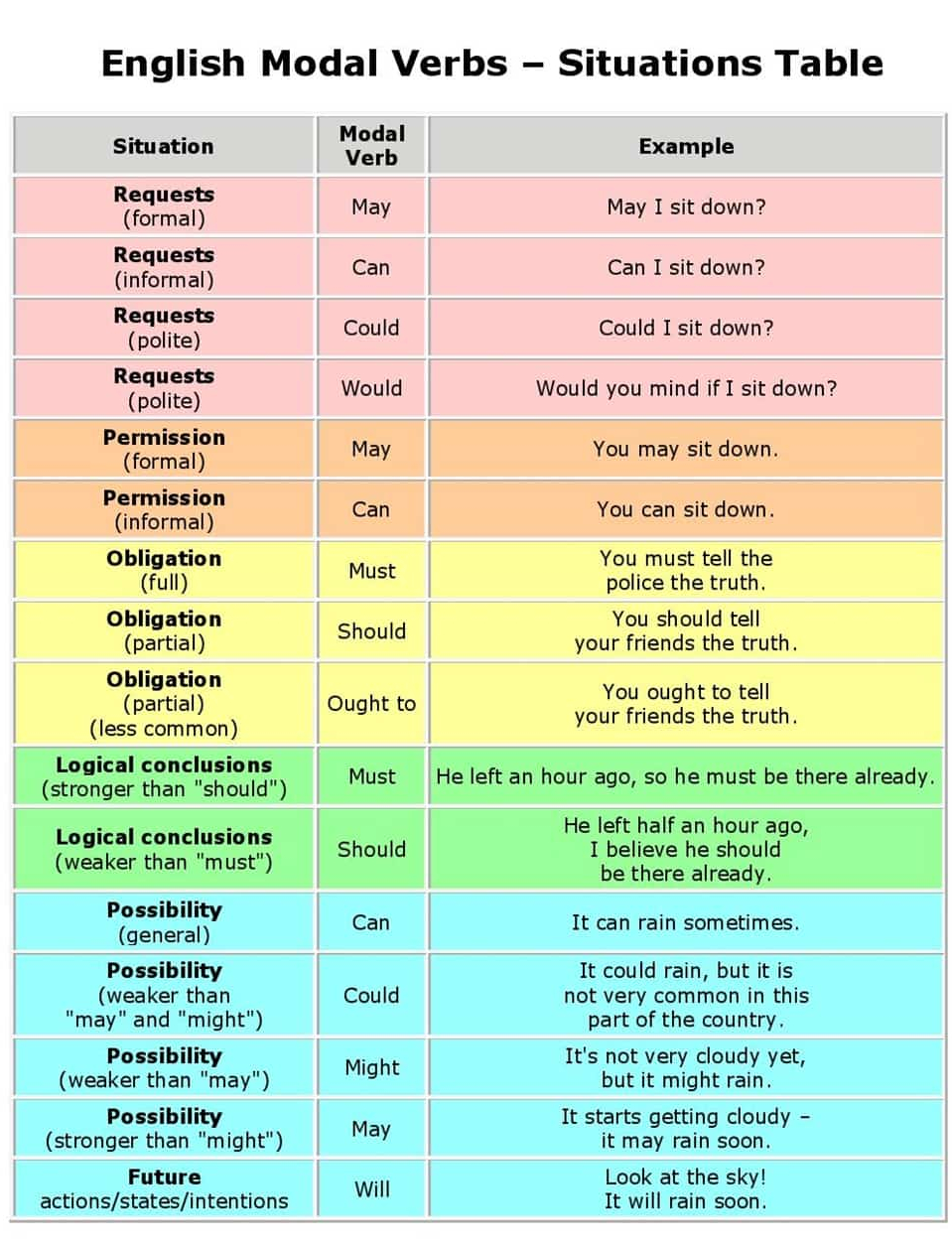
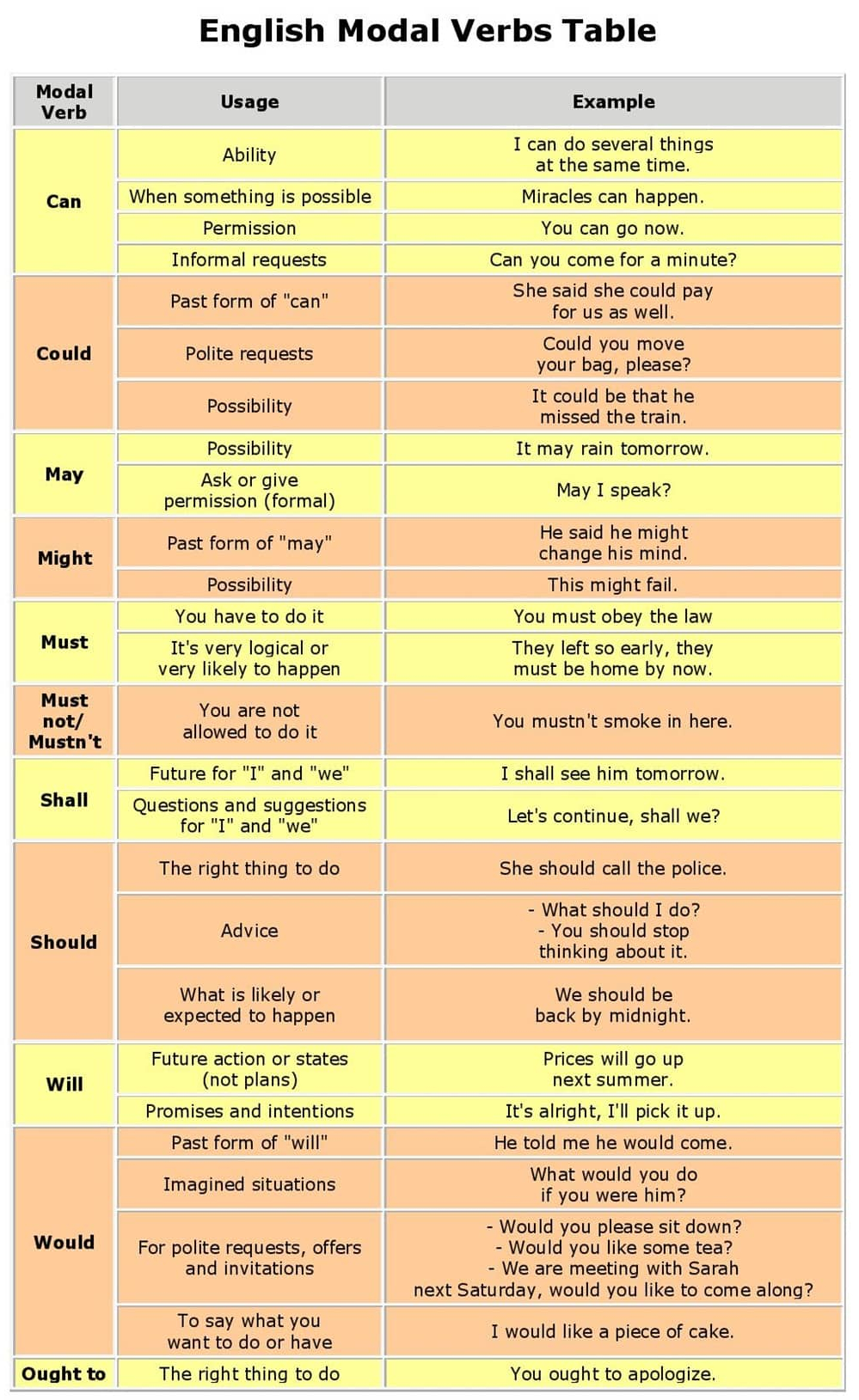
Modals are auxiliary verbs that indicate modality. Modality is the attitude or the connotation we want to express.
Modal verbs are used to express: ability, advice, obigation, prohibition, permission, possibility…..
Ability – can / could (in the past)
Obligation – must / have to
Prohibition – mustn’t / can’t
Absence of obligation – don’t have to / needn’t
Advice – should / ought to
Permission – may / can / could
Certainty – must
Probability – may / might / can / could
Examples
- Ability ➣He can speak several languages ➣I could jump when I was younger
- Obligation ➣You must stop at a red traffic light ➣I have to work
- Prohibition ➣We mustn’t tell him ➣You can’t smoke here
- Absence of obligation ➣She doesn’t have to do that ➣He needn’t buy it
- Advice ➣He should study more ➣She ought to eat less
- Permission ➣Can we come? ➣May I go to the toilet?
- Certainty ➣He must be very tired. He has been working hard
- Probability ➣It may / might rain tomorrow ➣This can / could be dangerous

reference: Valid Choice Burlington
KEY
A 1. has to – 2. must – 3. can – 4. mustn’t – 5. should – 6. might
B 1. mustn’t – 2. should – 3. don’t have to – 4. could – 5. might
C 1. You should compare prices... – 2. He might not know… – 3. They can’t help us. – 4. I couldn’t see… – 5. You don’t have to arrive…
Modal Perfect
Used to express situations in the past in a hypothetical way. The opportunity was not taken and the situation did not occur.
Form: modal verb + have + past participle

modal verbs in the past – reference: Valid Choice Burlington
KEY
D 1. may have – 2. should have – 3. could have – 4. must have – 5. shouldn’t have
E 1. b – 2. b – 3. a – 4. a – 5. a
F 1. could have stayed – 2. should see – 3. couldn’t find – 4. ought to have checked – 5. should have come – 6. must have left – 7. could go – 8. must be